

Take your digital presence further with Top-rated SEO Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Experience outstanding online performance through Social media and SEO Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Take your digital presence further with Digital presence Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Local SEO . Best SEO Parramatta Agency.Transform your business growth with Web design for startups Parramatta Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Choose excellence in digital marketing with SEO solutions Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Take your digital presence further with Modern web design Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
SEO Packages Parramatta .Maximise your business potential with Search engine marketing Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Online visibility Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Experience outstanding online performance through SEO maintenance Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Best Digital Marketing Parramatta Parramatta.

Take your digital presence further with Creative web design Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Transform your business growth with Parramatta local marketing experts Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Parramatta SEO growth Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Maximise your business potential with Website SEO tune-up Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Experience outstanding online performance through Parramatta web strategy Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Take your digital presence further with SEO-friendly websites Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business


Take your digital presence further with SEO ranking Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Take your digital presence further with Web design and development Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Experience outstanding online performance through Custom SEO campaigns Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Maximise your business potential with SEO tracking and reporting Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Transform your business growth with Full-service web design Parramatta Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Maximise your business potential with Affordable digital marketing Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta


In the Internet, a domain name is a string that identifies a realm of administrative autonomy, authority or control. Domain names are often used to identify services provided through the Internet, such as websites, email services and more. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and for application-specific naming and addressing purposes. In general, a domain name identifies a network domain or an Internet Protocol (IP) resource, such as a personal computer used to access the Internet, or a server computer.
Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS). Any name registered in the DNS is a domain name. Domain names are organized in subordinate levels (subdomains) of the DNS root domain, which is nameless. The first-level set of domain names are the top-level domains (TLDs), including the generic top-level domains (gTLDs), such as the prominent domains com, info, net, edu, and org, and the country code top-level domains (ccTLDs). Below these top-level domains in the DNS hierarchy are the second-level and third-level domain names that are typically open for reservation by end-users who wish to connect local area networks to the Internet, create other publicly accessible Internet resources or run websites, such as "wikipedia.org". The registration of a second- or third-level domain name is usually administered by a domain name registrar who sell its services to the public.
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is a domain name that is completely specified with all labels in the hierarchy of the DNS, having no parts omitted. Traditionally a FQDN ends in a dot (.) to denote the top of the DNS tree.[1] Labels in the Domain Name System are case-insensitive, and may therefore be written in any desired capitalization method, but most commonly domain names are written in lowercase in technical contexts.[2] A hostname is a domain name that has at least one associated IP address.
Domain names serve to identify Internet resources, such as computers, networks, and services, with a text-based label that is easier to memorize than the numerical addresses used in the Internet protocols. A domain name may represent entire collections of such resources or individual instances. Individual Internet host computers use domain names as host identifiers, also called hostnames. The term hostname is also used for the leaf labels in the domain name system, usually without further subordinate domain name space. Hostnames appear as a component in Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) for Internet resources such as websites (e.g., en.wikipedia.org).
Domain names are also used as simple identification labels to indicate ownership or control of a resource. Such examples are the realm identifiers used in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), the Domain Keys used to verify DNS domains in e-mail systems, and in many other Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs).
An important function of domain names is to provide easily recognizable and memorizable names to numerically addressed Internet resources. This abstraction allows any resource to be moved to a different physical location in the address topology of the network, globally or locally in an intranet. Such a move usually requires changing the IP address of a resource and the corresponding translation of this IP address to and from its domain name.
Domain names are used to establish a unique identity. Organizations can choose a domain name that corresponds to their name, helping Internet users to reach them easily.
A generic domain is a name that defines a general category, rather than a specific or personal instance, for example, the name of an industry, rather than a company name. Some examples of generic names are books.com, music.com, and travel.info. Companies have created brands based on generic names, and such generic domain names may be valuable.[3]
Domain names are often simply referred to as domains and domain name registrants are frequently referred to as domain owners, although domain name registration with a registrar does not confer any legal ownership of the domain name, only an exclusive right of use for a particular duration of time. The use of domain names in commerce may subject them to trademark law.
The practice of using a simple memorable abstraction of a host's numerical address on a computer network dates back to the ARPANET era, before the advent of today's commercial Internet. In the early network, each computer on the network retrieved the hosts file (host.txt) from a computer at SRI (now SRI International),[4][5] which mapped computer hostnames to numerical addresses. The rapid growth of the network made it impossible to maintain a centrally organized hostname registry and in 1983 the Domain Name System was introduced on the ARPANET and published by the Internet Engineering Task Force as RFC 882 and RFC 883.
The following table shows the first five .com domains with the dates of their registration:[6]
| Domain name | Registration date |
|---|---|
| symbolics.com | 15 March 1985 |
| bbn.com | 24 April 1985 |
| think.com | 24 May 1985 |
| mcc.com | 11 July 1985 |
| dec.com | 30 September 1985 |
and the first five .edu domains:[7]
| Domain name | Registration date |
|---|---|
| berkeley.edu | 24 April 1985 |
| cmu.edu | 24 April 1985 |
| purdue.edu | 24 April 1985 |
| rice.edu | 24 April 1985 |
| ucla.edu | 24 April 1985 |

Today, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) manages the top-level development and architecture of the Internet domain name space. It authorizes domain name registrars, through which domain names may be registered and reassigned.
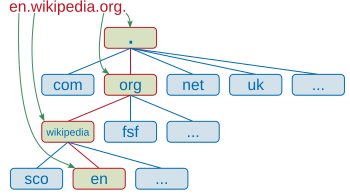
The domain name space consists of a tree of domain names. Each node in the tree holds information associated with the domain name. The tree sub-divides into zones beginning at the DNS root zone.
A domain name consists of one or more parts, technically called labels, that are conventionally concatenated, and delimited by dots, such as example.com.
When the Domain Name System was devised in the 1980s, the domain name space was divided into two main groups of domains.[9] The country code top-level domains (ccTLD) were primarily based on the two-character territory codes of ISO-3166 country abbreviations. In addition, a group of seven generic top-level domains (gTLD) was implemented which represented a set of categories of names and multi-organizations.[10] These were the domains gov, edu, com, mil, org, net, and int. These two types of top-level domains (TLDs) are the highest level of domain names of the Internet. Top-level domains form the DNS root zone of the hierarchical Domain Name System. Every domain name ends with a top-level domain label.
During the growth of the Internet, it became desirable to create additional generic top-level domains. As of October 2009, 21 generic top-level domains and 250 two-letter country-code top-level domains existed.[11] In addition, the ARPA domain serves technical purposes in the infrastructure of the Domain Name System.
During the 32nd International Public ICANN Meeting in Paris in 2008,[12] ICANN started a new process of TLD naming policy to take a "significant step forward on the introduction of new generic top-level domains." This program envisions the availability of many new or already proposed domains, as well as a new application and implementation process.[13] Observers believed that the new rules could result in hundreds of new top-level domains to be registered.[14] In 2012, the program commenced, and received 1930 applications.[15] By 2016, the milestone of 1000 live gTLD was reached.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains an annotated list of top-level domains in the DNS root zone database.[16]
For special purposes, such as network testing, documentation, and other applications, IANA also reserves a set of special-use domain names.[17] This list contains domain names such as example, local, localhost, and test. Other top-level domain names containing trade marks are registered for corporate use. Cases include brands such as BMW, Google, and Canon.[18]
Below the top-level domains in the domain name hierarchy are the second-level domain (SLD) names. These are the names directly to the left of .com, .net, and the other top-level domains. As an example, in the domain example.co.uk, co is the second-level domain.
Next are third-level domains, which are written immediately to the left of a second-level domain. There can be fourth- and fifth-level domains, and so on, with virtually no limitation. Each label is separated by a full stop (dot). An example of an operational domain name with four levels of domain labels is sos.state.oh.us. 'sos' is said to be a sub-domain of 'state.oh.us', and 'state' a sub-domain of 'oh.us', etc. In general, subdomains are domains subordinate to their parent domain. An example of very deep levels of subdomain ordering are the IPv6 reverse resolution DNS zones, e.g., 1.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.ip6.arpa, which is the reverse DNS resolution domain name for the IP address of a loopback interface, or the localhost name.
Second-level (or lower-level, depending on the established parent hierarchy) domain names are often created based on the name of a company (e.g., bbc.co.uk), product or service (e.g. hotmail.com). Below these levels, the next domain name component has been used to designate a particular host server. Therefore, ftp.example.com might be an FTP server, www.example.com would be a World Wide Web server, and mail.example.com could be an email server, each intended to perform only the implied function. Modern technology allows multiple physical servers with either different (cf. load balancing) or even identical addresses (cf. anycast) to serve a single hostname or domain name, or multiple domain names to be served by a single computer. The latter is very popular in Web hosting service centers, where service providers host the websites of many organizations on just a few servers.
The hierarchical DNS labels or components of domain names are separated in a fully qualified name by the full stop (dot, .).
The character set allowed in the Domain Name System is based on ASCII and does not allow the representation of names and words of many languages in their native scripts or alphabets. ICANN approved the Internationalized domain name (IDNA) system, which maps Unicode strings used in application user interfaces into the valid DNS character set by an encoding called Punycode. For example, københavn.eu is mapped to xn--kbenhavn-54a.eu. Many registries have adopted IDNA.
The first commercial Internet domain name, in the TLD com, was registered on 15 March 1985 in the name symbolics.com by Symbolics Inc., a computer systems firm in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
By 1992, fewer than 15,000 com domains had been registered.
In the first quarter of 2015, 294 million domain names had been registered.[19] A large fraction of them are in the com TLD, which as of December 21, 2014, had 115.6 million domain names,[20] including 11.9 million online business and e-commerce sites, 4.3 million entertainment sites, 3.1 million finance related sites, and 1.8 million sports sites.[21] As of July 15, 2012, the com TLD had more registrations than all of the ccTLDs combined.[22]
As of December 31, 2023,[update] 359.8 million domain names had been registered.[23]
The right to use a domain name is delegated by domain name registrars, which are accredited by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), the organization charged with overseeing the name and number systems of the Internet. In addition to ICANN, each top-level domain (TLD) is maintained and serviced technically by an administrative organization operating a registry. A registry is responsible for maintaining the database of names registered within the TLD it administers. The registry receives registration information from each domain name registrar authorized to assign names in the corresponding TLD and publishes the information using a special service, the WHOIS protocol.
Registries and registrars usually charge an annual fee for the service of delegating a domain name to a user and providing a default set of name servers. Often, this transaction is termed a sale or lease of the domain name, and the registrant may sometimes be called an "owner", but no such legal relationship is actually associated with the transaction, only the exclusive right to use the domain name. More correctly, authorized users are known as "registrants" or as "domain holders".
ICANN publishes the complete list of TLD registries and domain name registrars. Registrant information associated with domain names is maintained in an online database accessible with the WHOIS protocol. For most of the 250 country code top-level domains (ccTLDs), the domain registries maintain the WHOIS (Registrant, name servers, expiration dates, etc.) information.
Some domain name registries, often called network information centers (NIC), also function as registrars to end-users. The major generic top-level domain registries, such as for the com, net, org, info domains and others, use a registry-registrar model consisting of hundreds of domain name registrars (see lists at ICANN[24] or VeriSign).[25] In this method of management, the registry only manages the domain name database and the relationship with the registrars. The registrants (users of a domain name) are customers of the registrar, in some cases through additional layers of resellers.
There are also a few other alternative DNS root providers that try to compete or complement ICANN's role of domain name administration, however, most of them failed to receive wide recognition, and thus domain names offered by those alternative roots cannot be used universally on most other internet-connecting machines without additional dedicated configurations.
In the process of registering a domain name and maintaining authority over the new name space created, registrars use several key pieces of information connected with a domain:
A domain name consists of one or more labels, each of which is formed from the set of ASCII letters, digits, and hyphens (a–z, A–Z, 0–9, -), but not starting or ending with a hyphen. The labels are case-insensitive; for example, 'label' is equivalent to 'Label' or 'LABEL'. In the textual representation of a domain name, the labels are separated by a full stop (period).
Domain names are often seen in analogy to real estate in that domain names are foundations on which a website can be built, and the highest quality domain names, like sought-after real estate, tend to carry significant value, usually due to their online brand-building potential, use in advertising, search engine optimization, and many other criteria.
A few companies have offered low-cost, below-cost or even free domain registration with a variety of models adopted to recoup the costs to the provider. These usually require that domains be hosted on their website within a framework or portal that includes advertising wrapped around the domain holder's content, revenue from which allows the provider to recoup the costs. Domain registrations were free of charge when the DNS was new. A domain holder may provide an infinite number of subdomains in their domain. For example, the owner of example.org could provide subdomains such as foo.example.org and foo.bar.example.org to interested parties.
Many desirable domain names are already assigned and users must search for other acceptable names, using Web-based search features, or WHOIS and dig operating system tools. Many registrars have implemented domain name suggestion tools which search domain name databases and suggest available alternative domain names related to keywords provided by the user.
The business of resale of registered domain names is known as the domain aftermarket. Various factors influence the perceived value or market value of a domain name. Most of the high-prize domain sales are carried out privately.[26] Also, it is called confidential domain acquiring or anonymous domain acquiring.[27]
Intercapping is often used to emphasize the meaning of a domain name, because DNS names are not case-sensitive. Some names may be misinterpreted in certain uses of capitalization. For example: Who Represents, a database of artists and agents, chose whorepresents.com,[28] which can be misread. In such situations, the proper meaning may be clarified by placement of hyphens when registering a domain name. For instance, Experts Exchange, a programmers' discussion site, used expertsexchange.com, but changed its domain name to experts-exchange.com.[29]
The domain name is a component of a uniform resource locator (URL) used to access websites, for example:
A domain name may point to multiple IP addresses to provide server redundancy for the services offered, a feature that is used to manage the traffic of large, popular websites.
Web hosting services, on the other hand, run servers that are typically assigned only one or a few addresses while serving websites for many domains, a technique referred to as virtual web hosting. Such IP address overloading requires that each request identifies the domain name being referenced, for instance by using the HTTP request header field Host:, or Server Name Indication.
Critics often claim abuse of administrative power over domain names. Particularly noteworthy was the VeriSign Site Finder system which redirected all unregistered .com and .net domains to a VeriSign webpage. For example, at a public meeting with VeriSign to air technical concerns about Site Finder,[30] numerous people, active in the IETF and other technical bodies, explained how they were surprised by VeriSign's changing the fundamental behavior of a major component of Internet infrastructure, not having obtained the customary consensus. Site Finder, at first, assumed every Internet query was for a website, and it monetized queries for incorrect domain names, taking the user to VeriSign's search site. Other applications, such as many implementations of email, treat a lack of response to a domain name query as an indication that the domain does not exist, and that the message can be treated as undeliverable. The original VeriSign implementation broke this assumption for mail, because it would always resolve an erroneous domain name to that of Site Finder. While VeriSign later changed Site Finder's behaviour with regard to email, there was still widespread protest about VeriSign's action being more in its financial interest than in the interest of the Internet infrastructure component for which VeriSign was the steward.
Despite widespread criticism, VeriSign only reluctantly removed it after the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) threatened to revoke its contract to administer the root name servers. ICANN published the extensive set of letters exchanged, committee reports, and ICANN decisions.[31]
There is also significant disquiet regarding the United States Government's political influence over ICANN. This was a significant issue in the attempt to create a .xxx top-level domain and sparked greater interest in alternative DNS roots that would be beyond the control of any single country.[32]
Additionally, there are numerous accusations of domain name front running, whereby registrars, when given whois queries, automatically register the domain name for themselves. Network Solutions has been accused of this.[33]
In the United States, the Truth in Domain Names Act of 2003, in combination with the PROTECT Act of 2003, forbids the use of a misleading domain name with the intention of attracting Internet users into visiting Internet pornography sites.
The Truth in Domain Names Act follows the more general Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act passed in 1999 aimed at preventing typosquatting and deceptive use of names and trademarks in domain names.
In the early 21st century, the US Department of Justice (DOJ) pursued the seizure of domain names, based on the legal theory that domain names constitute property used to engage in criminal activity, and thus are subject to forfeiture. For example, in the seizure of the domain name of a gambling website, the DOJ referenced and .[34][1] In 2013 the US government seized Liberty Reserve, citing .[35]
The U.S. Congress passed the Combating Online Infringement and Counterfeits Act in 2010. Consumer Electronics Association vice president Michael Petricone was worried that seizure was a blunt instrument that could harm legitimate businesses.[36][37] After a joint operation on February 15, 2011, the DOJ and the Department of Homeland Security claimed to have seized ten domains of websites involved in advertising and distributing child pornography, but also mistakenly seized the domain name of a large DNS provider, temporarily replacing 84,000 websites with seizure notices.[38]
In the United Kingdom, the Police Intellectual Property Crime Unit (PIPCU) has been attempting to seize domain names from registrars without court orders.[39]
PIPCU and other UK law enforcement organisations make domain suspension requests to Nominet which they process on the basis of breach of terms and conditions. Around 16,000 domains are suspended annually, and about 80% of the requests originate from PIPCU.[40]
Because of the economic value it represents, the European Court of Human Rights has ruled that the exclusive right to a domain name is protected as property under article 1 of Protocol 1 to the European Convention on Human Rights.[41]
ICANN Business Constituency (BC) has spent decades trying to make IDN variants work at the second level, and in the last several years at the top level. Domain name variants are domain names recognized in different character encodings, like a single domain presented in traditional Chinese and simplified Chinese. It is an Internationalization and localization problem. Under Domain Name Variants, the different encodings of the domain name (in simplified and traditional Chinese) would resolve to the same host.[42][43]
According to John Levine, an expert on Internet related topics, "Unfortunately, variants don't work. The problem isn't putting them in the DNS, it's that once they're in the DNS, they don't work anywhere else."[42]
A fictitious domain name is a domain name used in a work of fiction or popular culture to refer to a domain that does not actually exist, often with invalid or unofficial top-level domains such as ".web", a usage exactly analogous to the dummy 555 telephone number prefix used in film and other media. The canonical fictitious domain name is "example.com", specifically set aside by IANA in RFC 2606 for such use, along with the .example TLD.
Domain names used in works of fiction have often been registered in the DNS, either by their creators or by cybersquatters attempting to profit from it. This phenomenon prompted NBC to purchase the domain name Hornymanatee.com after talk-show host Conan O'Brien spoke the name while ad-libbing on his show. O'Brien subsequently created a website based on the concept and used it as a running gag on the show.[44] Companies whose works have used fictitious domain names have also employed firms such as MarkMonitor to park fictional domain names in order to prevent misuse by third parties.[45]
Misspelled domain names, also known as typosquatting or URL hijacking, are domain names that are intentionally or unintentionally misspelled versions of popular or well-known domain names. The goal of misspelled domain names is to capitalize on internet users who accidentally type in a misspelled domain name, and are then redirected to a different website.
Misspelled domain names are often used for malicious purposes, such as phishing scams or distributing malware. In some cases, the owners of misspelled domain names may also attempt to sell the domain names to the owners of the legitimate domain names, or to individuals or organizations who are interested in capitalizing on the traffic generated by internet users who accidentally type in the misspelled domain names.
To avoid being caught by a misspelled domain name, internet users should be careful to type in domain names correctly, and should avoid clicking on links that appear suspicious or unfamiliar. Additionally, individuals and organizations who own popular or well-known domain names should consider registering common misspellings of their domain names in order to prevent others from using them for malicious purposes.
The term Domain name spoofing (or simply though less accurately, Domain spoofing) is used generically to describe one or more of a class of phishing attacks that depend on falsifying or misrepresenting an internet domain name.[46][47] These are designed to persuade unsuspecting users into visiting a web site other than that intended, or opening an email that is not in reality from the address shown (or apparently shown).[48] Although website and email spoofing attacks are more widely known, any service that relies on domain name resolution may be compromised.
There are a number of better-known types of domain spoofing:
A web directory or link directory is an online list or catalog of websites. That is, it is a directory on the World Wide Web of (all or part of) the World Wide Web. Historically, directories typically listed entries on people or businesses, and their contact information; such directories are still in use today. A web directory includes entries about websites, including links to those websites, organized into categories and subcategories.[1][2][3] Besides a link, each entry may include the title of the website, and a description of its contents. In most web directories, the entries are about whole websites, rather than individual pages within them (called "deep links"). Websites are often limited to inclusion in only a few categories.
There are two ways to find information on the Web: by searching or browsing. Web directories provide links in a structured list to make browsing easier. Many web directories combine searching and browsing by providing a search engine to search the directory. Unlike search engines, which base results on a database of entries gathered automatically by web crawler, most web directories are built manually by human editors. Many web directories allow site owners to submit their site for inclusion, and have editors review submissions for fitness.
Web directories may be general in scope, or limited to particular subjects or fields. Entries may be listed for free, or by paid submission (meaning the site owner must pay to have his or her website listed).
RSS directories are similar to web directories, but contain collections of RSS feeds, instead of links to websites.
During the early development of the web, there was a list of web servers edited by Tim Berners-Lee and hosted on the CERN webserver. One historical snapshot from 1992 remains.[4] He also created the World Wide Web Virtual Library, which is the oldest web directory.[5]
Most of the directories are general in on scope and list websites across a wide range of categories, regions and languages. But some niche directories focus on restricted regions, single languages, or specialist sectors. For example, there are shopping directories that specialize in the listing of retail e-commerce sites.
Examples of well-known general web directories are Yahoo! Directory (shut down at the end of 2014) and DMOZ (shut down on March 14, 2017). DMOZ was significant due to its extensive categorization and large number of listings and its free availability for use by other directories and search engines.[6]
However, a debate over the quality of directories and databases still continues, as search engines use DMOZ's content without real integration, and some experiment using clustering.
There have been many attempts to make building web directories easier, such as using automated submission of related links by script, or any number of available PHP portals and programs. Recently, social software techniques have spawned new efforts of categorization, with Amazon.com adding tagging to their product pages.
Directories have various features in their listings, often depending upon the price paid for inclusion:
rel="nofollow" attribute associated with the link, meaning search engines will give no weight to the linkA human-edited directory is created and maintained by editors who add links based on the policies particular to that directory. Human-edited directories are often targeted by SEOs on the basis that links from reputable sources will improve rankings in the major search engines. Some directories may prevent search engines from rating a displayed link by using redirects, nofollow attributes, or other techniques. Many human-edited directories, including DMOZ, World Wide Web Virtual Library, Business.com and Jasmine Directory, are edited by volunteers, who are often experts in particular categories. These directories are sometimes criticized due to long delays in approving submissions, or for rigid organizational structures and disputes among volunteer editors.
In response to these criticisms, some volunteer-edited directories have adopted wiki technology, to allow broader community participation in editing the directory (at the risk of introducing lower-quality, less objective entries).
Another direction taken by some web directories is the paid for inclusion model. This method enables the directory to offer timely inclusion for submissions and generally fewer listings as a result of the paid model. They often offer additional listing options to further enhance listings, including features listings and additional links to inner pages of the listed website. These options typically have an additional fee associated but offer significant help and visibility to sites and/or their inside pages.
Today submission of websites to web directories is considered a common SEO (search engine optimization) technique to get back-links for the submitted website. One distinctive feature of 'directory submission' is that it cannot be fully automated like search engine submissions. Manual directory submission is a tedious and time-consuming job and is often outsourced by webmasters.
Bid for Position directories, also known as bidding web directories, are paid-for-inclusion web directories where the listings of websites in the directory are ordered according to their bid amount. They are special in that the more a person pays, the higher up the list of websites in the directory they go. With the higher listing, the website becomes more visible and increases the chances that visitors who browse the directory will click on the listing.
Web directories will often make themselves accessing by more and more URLs by acquiring the domain registrations of defunct websites as soon as they expire, a practice known as Domain drop catching.
Reciprocal links may not help with competitive keyword rankings, but that does not mean you should avoid them when they make sound business sense. What you should definitely avoid are manipulative reciprocal linking schemes like automated link trading programs and three-way links or four-way links.
Web design encompasses many different skills and disciplines in the production and maintenance of websites. The different areas of web design include web graphic design; user interface design (UI design); authoring, including standardised code and proprietary software; user experience design (UX design); and search engine optimization. Often many individuals will work in teams covering different aspects of the design process, although some designers will cover them all.[1] The term "web design" is normally used to describe the design process relating to the front-end (client side) design of a website including writing markup. Web design partially overlaps web engineering in the broader scope of web development. Web designers are expected to have an awareness of usability and be up to date with web accessibility guidelines.

Although web design has a fairly recent history, it can be linked to other areas such as graphic design, user experience, and multimedia arts, but is more aptly seen from a technological standpoint. It has become a large part of people's everyday lives. It is hard to imagine the Internet without animated graphics, different styles of typography, backgrounds, videos and music. The web was announced on August 6, 1991; in November 1992, CERN was the first website to go live on the World Wide Web. During this period, websites were structured by using the <table> tag which created numbers on the website. Eventually, web designers were able to find their way around it to create more structures and formats. In early history, the structure of the websites was fragile and hard to contain, so it became very difficult to use them. In November 1993, ALIWEB was the first ever search engine to be created (Archie Like Indexing for the WEB).[2]
In 1989, whilst working at CERN in Switzerland, British scientist Tim Berners-Lee proposed to create a global hypertext project, which later became known as the World Wide Web. From 1991 to 1993 the World Wide Web was born. Text-only HTML pages could be viewed using a simple line-mode web browser.[3] In 1993 Marc Andreessen and Eric Bina, created the Mosaic browser. At the time there were multiple browsers, however the majority of them were Unix-based and naturally text-heavy. There had been no integrated approach to graphic design elements such as images or sounds. The Mosaic browser broke this mould.[4] The W3C was created in October 1994 to "lead the World Wide Web to its full potential by developing common protocols that promote its evolution and ensure its interoperability."[5] This discouraged any one company from monopolizing a proprietary browser and programming language, which could have altered the effect of the World Wide Web as a whole. The W3C continues to set standards, which can today be seen with JavaScript and other languages. In 1994 Andreessen formed Mosaic Communications Corp. that later became known as Netscape Communications, the Netscape 0.9 browser. Netscape created its HTML tags without regard to the traditional standards process. For example, Netscape 1.1 included tags for changing background colours and formatting text with tables on web pages. From 1996 to 1999 the browser wars began, as Microsoft and Netscape fought for ultimate browser dominance. During this time there were many new technologies in the field, notably Cascading Style Sheets, JavaScript, and Dynamic HTML. On the whole, the browser competition did lead to many positive creations and helped web design evolve at a rapid pace.[6]
In 1996, Microsoft released its first competitive browser, which was complete with its features and HTML tags. It was also the first browser to support style sheets, which at the time was seen as an obscure authoring technique and is today an important aspect of web design.[6] The HTML markup for tables was originally intended for displaying tabular data. However, designers quickly realized the potential of using HTML tables for creating complex, multi-column layouts that were otherwise not possible. At this time, as design and good aesthetics seemed to take precedence over good markup structure, little attention was paid to semantics and web accessibility. HTML sites were limited in their design options, even more so with earlier versions of HTML. To create complex designs, many web designers had to use complicated table structures or even use blank spacer .GIF images to stop empty table cells from collapsing.[7] CSS was introduced in December 1996 by the W3C to support presentation and layout. This allowed HTML code to be semantic rather than both semantic and presentational and improved web accessibility, see tableless web design.
In 1996, Flash (originally known as FutureSplash) was developed. At the time, the Flash content development tool was relatively simple compared to now, using basic layout and drawing tools, a limited precursor to ActionScript, and a timeline, but it enabled web designers to go beyond the point of HTML, animated GIFs and JavaScript. However, because Flash required a plug-in, many web developers avoided using it for fear of limiting their market share due to lack of compatibility. Instead, designers reverted to GIF animations (if they did not forego using motion graphics altogether) and JavaScript for widgets. But the benefits of Flash made it popular enough among specific target markets to eventually work its way to the vast majority of browsers, and powerful enough to be used to develop entire sites.[7]
In 1998, Netscape released Netscape Communicator code under an open-source licence, enabling thousands of developers to participate in improving the software. However, these developers decided to start a standard for the web from scratch, which guided the development of the open-source browser and soon expanded to a complete application platform.[6] The Web Standards Project was formed and promoted browser compliance with HTML and CSS standards. Programs like Acid1, Acid2, and Acid3 were created in order to test browsers for compliance with web standards. In 2000, Internet Explorer was released for Mac, which was the first browser that fully supported HTML 4.01 and CSS 1. It was also the first browser to fully support the PNG image format.[6] By 2001, after a campaign by Microsoft to popularize Internet Explorer, Internet Explorer had reached 96% of web browser usage share, which signified the end of the first browser wars as Internet Explorer had no real competition.[8]
Since the start of the 21st century, the web has become more and more integrated into people's lives. As this has happened the technology of the web has also moved on. There have also been significant changes in the way people use and access the web, and this has changed how sites are designed.
Since the end of the browsers wars[when?] new browsers have been released. Many of these are open source, meaning that they tend to have faster development and are more supportive of new standards. The new options are considered by many[weasel words] to be better than Microsoft's Internet Explorer.
The W3C has released new standards for HTML (HTML5) and CSS (CSS3), as well as new JavaScript APIs, each as a new but individual standard.[when?] While the term HTML5 is only used to refer to the new version of HTML and some of the JavaScript APIs, it has become common to use it to refer to the entire suite of new standards (HTML5, CSS3 and JavaScript).
With the advancements in 3G and LTE internet coverage, a significant portion of website traffic shifted to mobile devices. This shift influenced the web design industry, steering it towards a minimalist, lighter, and more simplistic style. The "mobile first" approach emerged as a result, emphasizing the creation of website designs that prioritize mobile-oriented layouts first, before adapting them to larger screen dimensions.
Web designers use a variety of different tools depending on what part of the production process they are involved in. These tools are updated over time by newer standards and software but the principles behind them remain the same. Web designers use both vector and raster graphics editors to create web-formatted imagery or design prototypes. A website can be created using WYSIWYG website builder software or a content management system, or the individual web pages can be hand-coded in just the same manner as the first web pages were created. Other tools web designers might use include markup validators[9] and other testing tools for usability and accessibility to ensure their websites meet web accessibility guidelines.[10]
One popular tool in web design is UX Design, a type of art that designs products to perform an accurate user background. UX design is very deep. UX is more than the web, it is very independent, and its fundamentals can be applied to many other browsers or apps. Web design is mostly based on web-based things. UX can overlap both web design and design. UX design mostly focuses on products that are less web-based.[11]
Marketing and communication design on a website may identify what works for its target market. This can be an age group or particular strand of culture; thus the designer may understand the trends of its audience. Designers may also understand the type of website they are designing, meaning, for example, that (B2B) business-to-business website design considerations might differ greatly from a consumer-targeted website such as a retail or entertainment website. Careful consideration might be made to ensure that the aesthetics or overall design of a site do not clash with the clarity and accuracy of the content or the ease of web navigation,[12] especially on a B2B website. Designers may also consider the reputation of the owner or business the site is representing to make sure they are portrayed favorably. Web designers normally oversee all the websites that are made on how they work or operate on things. They constantly are updating and changing everything on websites behind the scenes. All the elements they do are text, photos, graphics, and layout of the web. Before beginning work on a website, web designers normally set an appointment with their clients to discuss layout, colour, graphics, and design. Web designers spend the majority of their time designing websites and making sure the speed is right. Web designers typically engage in testing and working, marketing, and communicating with other designers about laying out the websites and finding the right elements for the websites.[13]
User understanding of the content of a website often depends on user understanding of how the website works. This is part of the user experience design. User experience is related to layout, clear instructions, and labeling on a website. How well a user understands how they can interact on a site may also depend on the interactive design of the site. If a user perceives the usefulness of the website, they are more likely to continue using it. Users who are skilled and well versed in website use may find a more distinctive, yet less intuitive or less user-friendly website interface useful nonetheless. However, users with less experience are less likely to see the advantages or usefulness of a less intuitive website interface. This drives the trend for a more universal user experience and ease of access to accommodate as many users as possible regardless of user skill.[14] Much of the user experience design and interactive design are considered in the user interface design.
Advanced interactive functions may require plug-ins if not advanced coding language skills. Choosing whether or not to use interactivity that requires plug-ins is a critical decision in user experience design. If the plug-in doesn't come pre-installed with most browsers, there's a risk that the user will have neither the know-how nor the patience to install a plug-in just to access the content. If the function requires advanced coding language skills, it may be too costly in either time or money to code compared to the amount of enhancement the function will add to the user experience. There's also a risk that advanced interactivity may be incompatible with older browsers or hardware configurations. Publishing a function that doesn't work reliably is potentially worse for the user experience than making no attempt. It depends on the target audience if it's likely to be needed or worth any risks.

Progressive enhancement is a strategy in web design that puts emphasis on web content first, allowing everyone to access the basic content and functionality of a web page, whilst users with additional browser features or faster Internet access receive the enhanced version instead.
In practice, this means serving content through HTML and applying styling and animation through CSS to the technically possible extent, then applying further enhancements through JavaScript. Pages' text is loaded immediately through the HTML source code rather than having to wait for JavaScript to initiate and load the content subsequently, which allows content to be readable with minimum loading time and bandwidth, and through text-based browsers, and maximizes backwards compatibility.[15]
As an example, MediaWiki-based sites including Wikipedia use progressive enhancement, as they remain usable while JavaScript and even CSS is deactivated, as pages' content is included in the page's HTML source code, whereas counter-example Everipedia relies on JavaScript to load pages' content subsequently; a blank page appears with JavaScript deactivated.
Part of the user interface design is affected by the quality of the page layout. For example, a designer may consider whether the site's page layout should remain consistent on different pages when designing the layout. Page pixel width may also be considered vital for aligning objects in the layout design. The most popular fixed-width websites generally have the same set width to match the current most popular browser window, at the current most popular screen resolution, on the current most popular monitor size. Most pages are also center-aligned for concerns of aesthetics on larger screens.
Fluid layouts increased in popularity around 2000 to allow the browser to make user-specific layout adjustments to fluid layouts based on the details of the reader's screen (window size, font size relative to window, etc.). They grew as an alternative to HTML-table-based layouts and grid-based design in both page layout design principles and in coding technique but were very slow to be adopted.[note 1] This was due to considerations of screen reading devices and varying windows sizes which designers have no control over. Accordingly, a design may be broken down into units (sidebars, content blocks, embedded advertising areas, navigation areas) that are sent to the browser and which will be fitted into the display window by the browser, as best it can. Although such a display may often change the relative position of major content units, sidebars may be displaced below body text rather than to the side of it. This is a more flexible display than a hard-coded grid-based layout that doesn't fit the device window. In particular, the relative position of content blocks may change while leaving the content within the block unaffected. This also minimizes the user's need to horizontally scroll the page.
Responsive web design is a newer approach, based on CSS3, and a deeper level of per-device specification within the page's style sheet through an enhanced use of the CSS @media rule. In March 2018 Google announced they would be rolling out mobile-first indexing.[16] Sites using responsive design are well placed to ensure they meet this new approach.
Web designers may choose to limit the variety of website typefaces to only a few which are of a similar style, instead of using a wide range of typefaces or type styles. Most browsers recognize a specific number of safe fonts, which designers mainly use in order to avoid complications.
Font downloading was later included in the CSS3 fonts module and has since been implemented in Safari 3.1, Opera 10, and Mozilla Firefox 3.5. This has subsequently increased interest in web typography, as well as the usage of font downloading.
Most site layouts incorporate negative space to break the text up into paragraphs and also avoid center-aligned text.[17]
The page layout and user interface may also be affected by the use of motion graphics. The choice of whether or not to use motion graphics may depend on the target market for the website. Motion graphics may be expected or at least better received with an entertainment-oriented website. However, a website target audience with a more serious or formal interest (such as business, community, or government) might find animations unnecessary and distracting if only for entertainment or decoration purposes. This doesn't mean that more serious content couldn't be enhanced with animated or video presentations that is relevant to the content. In either case, motion graphic design may make the difference between more effective visuals or distracting visuals.
Motion graphics that are not initiated by the site visitor can produce accessibility issues. The World Wide Web consortium accessibility standards require that site visitors be able to disable the animations.[18]
Website designers may consider it to be good practice to conform to standards. This is usually done via a description specifying what the element is doing. Failure to conform to standards may not make a website unusable or error-prone, but standards can relate to the correct layout of pages for readability as well as making sure coded elements are closed appropriately. This includes errors in code, a more organized layout for code, and making sure IDs and classes are identified properly. Poorly coded pages are sometimes colloquially called tag soup. Validating via W3C[9] can only be done when a correct DOCTYPE declaration is made, which is used to highlight errors in code. The system identifies the errors and areas that do not conform to web design standards. This information can then be corrected by the user.[19]
There are two ways websites are generated: statically or dynamically.
A static website stores a unique file for every page of a static website. Each time that page is requested, the same content is returned. This content is created once, during the design of the website. It is usually manually authored, although some sites use an automated creation process, similar to a dynamic website, whose results are stored long-term as completed pages. These automatically created static sites became more popular around 2015, with generators such as Jekyll and Adobe Muse.[20]
The benefits of a static website are that they were simpler to host, as their server only needed to serve static content, not execute server-side scripts. This required less server administration and had less chance of exposing security holes. They could also serve pages more quickly, on low-cost server hardware. This advantage became less important as cheap web hosting expanded to also offer dynamic features, and virtual servers offered high performance for short intervals at low cost.
Almost all websites have some static content, as supporting assets such as images and style sheets are usually static, even on a website with highly dynamic pages.
Dynamic websites are generated on the fly and use server-side technology to generate web pages. They typically extract their content from one or more back-end databases: some are database queries across a relational database to query a catalog or to summarise numeric information, and others may use a document database such as MongoDB or NoSQL to store larger units of content, such as blog posts or wiki articles.
In the design process, dynamic pages are often mocked-up or wireframed using static pages. The skillset needed to develop dynamic web pages is much broader than for a static page, involving server-side and database coding as well as client-side interface design. Even medium-sized dynamic projects are thus almost always a team effort.
When dynamic web pages first developed, they were typically coded directly in languages such as Perl, PHP or ASP. Some of these, notably PHP and ASP, used a 'template' approach where a server-side page resembled the structure of the completed client-side page, and data was inserted into places defined by 'tags'. This was a quicker means of development than coding in a purely procedural coding language such as Perl.
Both of these approaches have now been supplanted for many websites by higher-level application-focused tools such as content management systems. These build on top of general-purpose coding platforms and assume that a website exists to offer content according to one of several well-recognised models, such as a time-sequenced blog, a thematic magazine or news site, a wiki, or a user forum. These tools make the implementation of such a site very easy, and a purely organizational and design-based task, without requiring any coding.
Editing the content itself (as well as the template page) can be done both by means of the site itself and with the use of third-party software. The ability to edit all pages is provided only to a specific category of users (for example, administrators, or registered users). In some cases, anonymous users are allowed to edit certain web content, which is less frequent (for example, on forums - adding messages). An example of a site with an anonymous change is Wikipedia.
Usability experts, including Jakob Nielsen and Kyle Soucy, have often emphasised homepage design for website success and asserted that the homepage is the most important page on a website.[21] Nielsen, Jakob; Tahir, Marie (October 2001), Homepage Usability: 50 Websites Deconstructed, New Riders Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7357-1102-0[22][23] However practitioners into the 2000s were starting to find that a growing number of website traffic was bypassing the homepage, going directly to internal content pages through search engines, e-newsletters and RSS feeds.[24] This led many practitioners to argue that homepages are less important than most people think.[25][26][27][28] Jared Spool argued in 2007 that a site's homepage was actually the least important page on a website.[29]
In 2012 and 2013, carousels (also called 'sliders' and 'rotating banners') have become an extremely popular design element on homepages, often used to showcase featured or recent content in a confined space.[30] Many practitioners argue that carousels are an ineffective design element and hurt a website's search engine optimisation and usability.[30][31][32]
There are two primary jobs involved in creating a website: the web designer and web developer, who often work closely together on a website.[33] The web designers are responsible for the visual aspect, which includes the layout, colouring, and typography of a web page. Web designers will also have a working knowledge of markup languages such as HTML and CSS, although the extent of their knowledge will differ from one web designer to another. Particularly in smaller organizations, one person will need the necessary skills for designing and programming the full web page, while larger organizations may have a web designer responsible for the visual aspect alone.
Further jobs which may become involved in the creation of a website include:
Chat GPT and other AI models are being used to write and code websites making it faster and easier to create websites. There are still discussions about the ethical implications on using artificial intelligence for design as the world becomes more familiar with using AI for time-consuming tasks used in design processes.[34]
<table>-based markup and spacer .GIF imagescite web: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)cite web: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)